Agave plant health benefits extend far beyond its sweet nectar. This remarkable plant, a staple in many cultures, offers a surprising array of potential health advantages, from aiding digestion to potentially managing blood sugar. We’ll explore the nutritional powerhouse that is agave, examining its unique composition and its impact on overall well-being, while also acknowledging potential drawbacks and the importance of moderation.
We’ll delve into the science behind agave’s purported benefits, comparing it to other sweeteners and examining the evidence supporting its traditional medicinal uses. From its prebiotic properties to its antioxidant capacity, we’ll uncover the multifaceted nature of this often-overlooked plant and its potential role in a healthy lifestyle.
Get ready to discover the hidden potential within the agave plant.
Agave: A Deep Dive into its Nutritional and Health Benefits

Agave, a succulent plant known for its sweet nectar, has gained popularity as a natural sweetener. But beyond its sweetness, agave offers a surprising array of potential health benefits, stemming from its unique nutritional profile and bioactive compounds. This article explores the nutritional value, impact on blood sugar, digestive health benefits, antioxidant properties, potential risks, traditional uses, and a visual representation of agave’s multifaceted contributions to well-being.
Nutritional Value of Agave
Agave nectar boasts a complex nutritional composition. While primarily known for its high fructose content, it also contains various vitamins and minerals, contributing to its potential health benefits. Compared to other sweeteners like refined sugar or high-fructose corn syrup, agave offers a slightly different nutritional profile, though moderation remains key.
| Nutrient | Agave Nectar (per 100g) | Refined Sugar (per 100g) | High-Fructose Corn Syrup (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 310 | 387 | 387 |
| Carbohydrates | 78g | 99.9g | 99.9g |
| Fructose | ~50-60% | 0% | ~55% |
| Glucose | ~20-30% | 0% | ~45% |
| Potassium | Trace amounts | 0 | 0 |
| Calcium | Trace amounts | 0 | 0 |
While trace amounts of vitamins and minerals are present, agave’s primary nutritional contribution is its carbohydrate content, primarily in the form of fructose and glucose.
Agave’s Role in Blood Sugar Management
Agave’s glycemic index (GI) is a subject of ongoing discussion. While some studies suggest a moderate GI, others indicate a potentially higher GI depending on the processing methods and type of agave. This variability underscores the importance of considering individual responses and blood sugar monitoring when incorporating agave into a diet, particularly for individuals with diabetes.
Compared to other sweeteners, agave’s impact on blood sugar levels can vary significantly.
Research on agave’s impact on insulin sensitivity is limited. More comprehensive studies are needed to draw definitive conclusions.
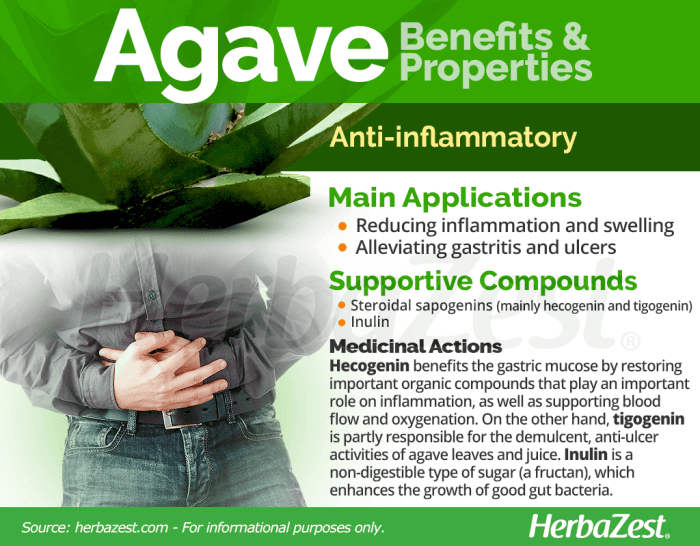
Agave and Digestive Health
Agave’s prebiotic properties are linked to its inulin content, a type of fructan fiber. Inulin acts as a food source for beneficial gut bacteria, promoting a healthy gut microbiome. This can contribute to improved digestion and overall gut health. For individuals with digestive issues like constipation or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), incorporating agave in moderation might offer some relief, although individual responses can vary greatly.
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Kimchi
- Sauerkraut
These foods, rich in probiotics, synergistically enhance the benefits of agave’s prebiotic properties.
Agave’s Antioxidant Properties, Agave plant health benefits
Agave contains various antioxidant compounds, including polyphenols, which help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. These antioxidants contribute to the body’s defense against oxidative stress, a process linked to various chronic diseases. While agave’s antioxidant capacity might not match that of some potent antioxidant-rich foods, it still contributes to overall antioxidant intake.
Agave’s antioxidant properties might play a beneficial role in preventing or managing diseases associated with oxidative stress, such as cardiovascular disease and certain types of cancer. However, it’s crucial to remember that agave should not be considered a primary treatment for any disease.
Potential Risks and Considerations of Agave Consumption
Excessive agave consumption can lead to several potential health risks. Its high fructose content, if consumed in large quantities, can contribute to weight gain, metabolic syndrome, and liver problems. Moderation is essential to reap the potential benefits of agave without compromising overall health.
| Risk | Description | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| High Fructose Content | Can contribute to metabolic issues if consumed excessively. | Moderate intake. |
| Weight Gain | High caloric density can lead to weight gain if not balanced with overall diet. | Consume as part of a balanced diet. |
| Glycemic Impact | Can affect blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals with diabetes. | Monitor blood sugar levels. |
| Recommended Daily Intake | No universally agreed-upon daily limit; moderation is key. | Consult a healthcare professional. |
Agave in Traditional Medicine
Agave has a long history of use in traditional medicine, particularly in Mexico and parts of Central America. It has been used for various purposes, including wound healing, pain relief, and digestive aid. While some traditional uses have some scientific backing, further research is needed to validate many of these claims.
Agave’s cultural significance extends beyond its medicinal applications, often holding symbolic and ritualistic importance in various indigenous communities.
Visual Representation of Agave’s Health Benefits
Imagine an illustration where a vibrant agave plant is central, its roots extending deep into the earth, symbolizing its grounding and nourishing properties. The leaves could be depicted in shades of green and blue-green, representing growth and vitality. From the plant, various pathways branch out, each representing a health benefit: a bright yellow pathway for energy, a deep blue pathway for antioxidant protection, a reddish-brown pathway for digestive health (with friendly gut bacteria depicted along it), and a balanced pathway for blood sugar management.
The colors and shapes are chosen to be visually appealing and easily understandable, connecting the visual elements to the specific health benefits.
A separate image could show the different parts of the agave plant – the leaves (for nectar and fiber), the heart (for certain culinary uses), and the roots (potentially for medicinal applications). Each part would be labeled with its corresponding health benefits and uses, creating a visually engaging representation of the agave plant’s holistic contributions to well-being.
Final Review
Ultimately, while agave offers potential health benefits, responsible consumption is key. Understanding its nutritional profile, glycemic impact, and potential drawbacks allows for informed choices. Whether you’re drawn to its sweetness, its digestive support, or its rich history in traditional medicine, agave presents a compelling case for further exploration and mindful integration into a balanced diet.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
FAQ Compilation: Agave Plant Health Benefits
Is agave suitable for everyone?
While generally safe, individuals with fructose intolerance or diabetes should consume agave cautiously and in moderation. Always consult a doctor before making significant dietary changes.
How does agave compare to honey or maple syrup?
Agave has a higher fructose content than honey or maple syrup, impacting its glycemic index and potential effects on blood sugar. Nutritional profiles also vary significantly.
Can agave help with weight loss?
There’s no conclusive evidence that agave directly aids weight loss. Like any sweetener, moderation is key to prevent weight gain.
What are the best ways to use agave?
Agave can be used as a sweetener in beverages, baked goods, and sauces. Its mild flavor pairs well with many dishes.






